Django forms
The Django Form class
At the heart of this system of components is Django’s Form class. In much the same way that a Django model describes the logical structure of an object, its behavior, and the way its parts are represented to us, a Form class describes a form and determines how it works and appears.
In a similar way that a model class’s fields map to database fields, a form class’s fields map to HTML form input elements. (A ModelForm maps a model class’s fields to HTML form input elements via a Form; this is what the Django admin is based upon.)
A form’s fields are themselves classes; they manage form data and perform validation when a form is submitted. A DateField and a FileField handle very different kinds of data and have to do different things with it.
A form field is represented to a user in the browser as an HTML “widget” - a piece of user interface machinery. Each field type has an appropriate default Widget class, but these can be overridden as required.
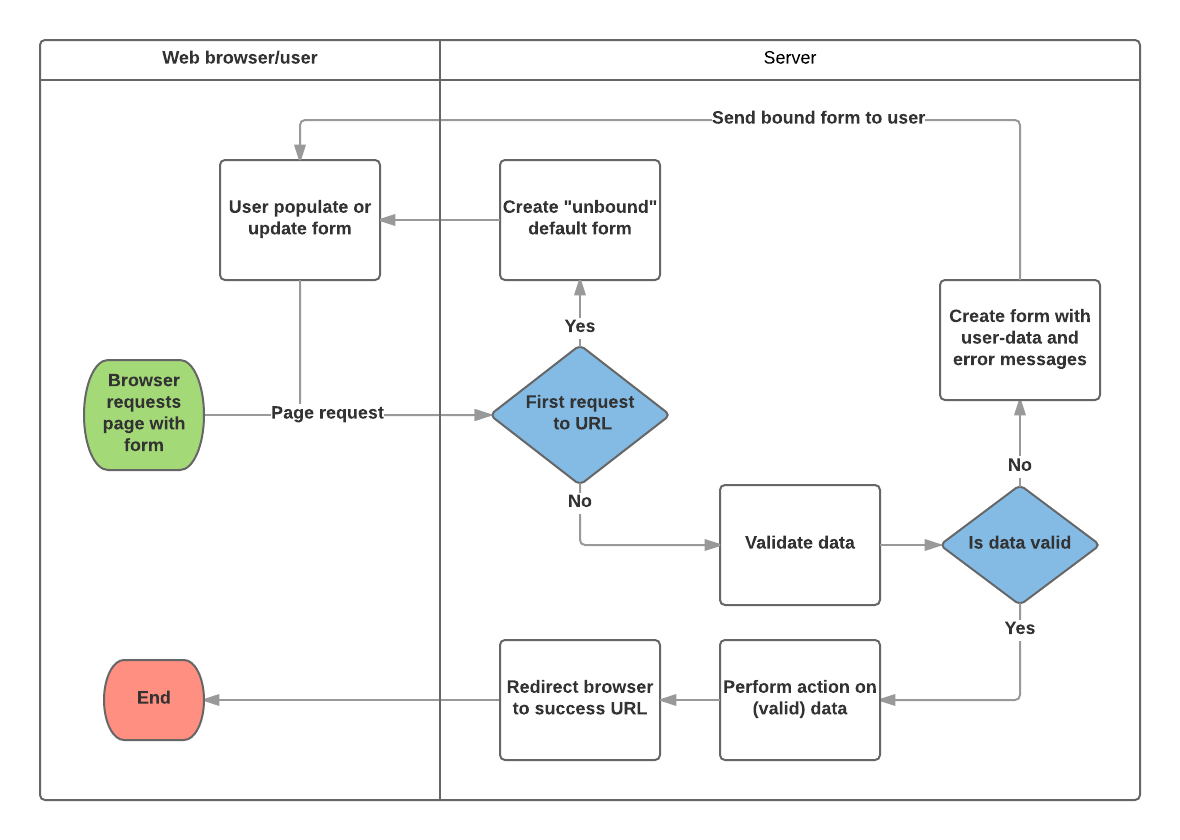
Building a form in Django
from django import forms
class NameForm(forms.Form):
your_name = forms.CharField(label='Your name', max_length=100)
The view
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect
from django.shortcuts import render
from .forms import NameForm
def get_name(request):
# if this is a POST request we need to process the form data
if request.method == 'POST':
# create a form instance and populate it with data from the request:
form = NameForm(request.POST)
# check whether it's valid:
if form.is_valid():
# process the data in form.cleaned_data as required
# ...
# redirect to a new URL:
return HttpResponseRedirect('/thanks/')
# if a GET (or any other method) we'll create a blank form
else:
form = NameForm()
return render(request, 'name.html', {'form': form})
Note
All form classes are created as subclasses of either django.forms.Form or django.forms.ModelForm. You can think of ModelForm as a subclass of Form. Form and ModelForm actually inherit common functionality from a (private) BaseForm class, but this implementation detail is rarely important.